The authors enrolled patients with treatment-naïve nccRCC and treated them with nivolumab 240mg IV every 2 weeks for 6 doses followed by 360mg IV every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by 480 mg every 4 weeks until progressive disease (PD), toxicity, or completion of 96 weeks of treatment (Part A; n=16). Patients who had progressive disease or who, at 48 weeks, had stable disease, were potentially eligible to receive salvage nivolumab (3mg/kg) and ipilimumab (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by nivolumab maintenance every 4 weeks for up to 48 weeks (Part B; n=19). Biopsy of a metastatic lesion obtained within 12 months prior to study entry and prior to enrolling on Part B was used for correlative studies.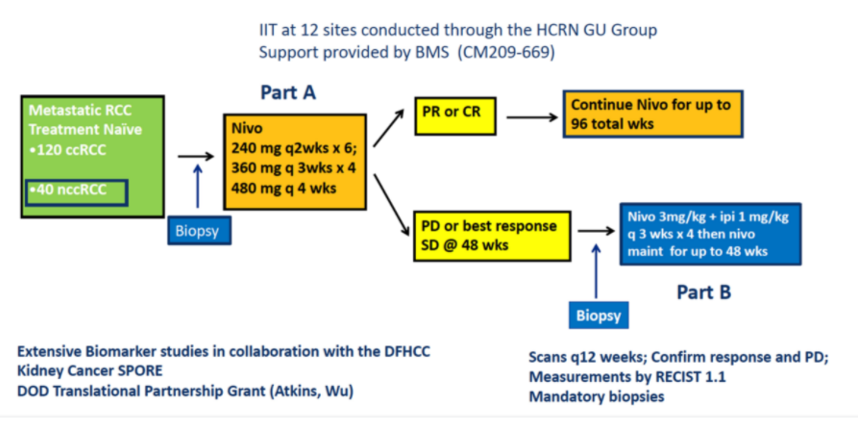
Thirty-five patients with nccRCC were enrolled between May 2017 and December 2019 across 12 different participating HCRN sites. The median age of enrolled patients was 63 years (range 35-84 years) and 89%, male. In terms of disease risk characteristics, 8 (23%) patients had favorable, 18 (51%) intermediate, and 9 (26%) poor-risk disease per IMDC criteria. In terms of histology, 19 (54%) patients had papillary RCC, 6 (17%) had chromophobe RCC, and 10 (29%) had unclassified histology.
In terms of treatment response, RECIST defined ORR was seen in 5 of 35 patients (14.3%) with a complete response (CR) in 2 (5.7%) and a partial response (PR) in 3 (8.6%). Stable disease was seen in 16 (45.7%) patients while 14 (40.0%) had progressive disease. Immune-related ORR was 8 of 35 (22.9%).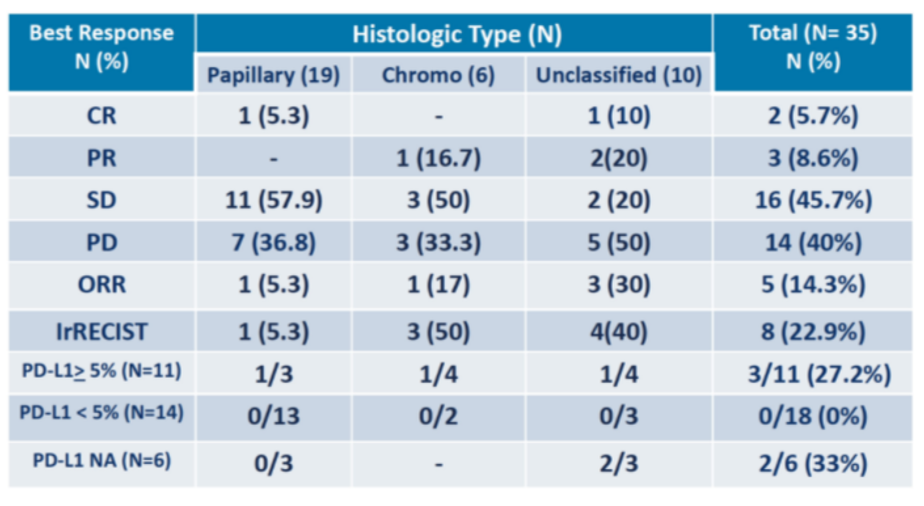
The authors then assessed RECIST ORR according to histology. In those with papillary RCC, the response rate was 1/19 (5%) while for those with chromophobe, ORR was 1/6 (17%) and it was 3/10 (30%) in those with unclassified RCC. Among 9 patients (26%) with tumors with sarcomatoid features, 3 (33%) responded (2 unclassified, 1 papillary). Further, ORR by PD-L1 status showed an ORR of 33% in those with 5-20% PD-L1 expression and 25% in those with >20% PD-L1 expression.
The median progression-free survival was 4.0 months (95% CI 2.8- 4.3). At the time of reporting, 21 of 35 patients remained alive and none of the responders had progressed or died.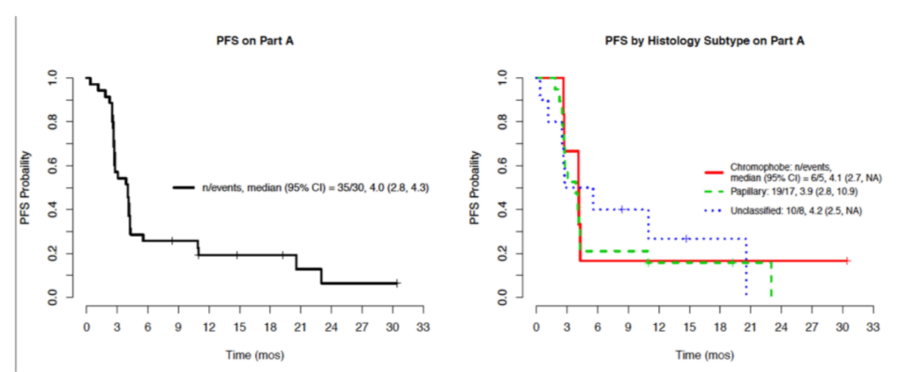
Among the 30 patients with progressive disease and 3 with stable disease at 48 weeks who were potentially eligible for salvage nivolumab and ipilimumab (Part B), 13 did not enroll due to symptomatic progressive disease (6), grade 3-4 nivolumab-related toxicity (3), or other reasons (4). Among the 17 patients who enrolled for salvage therapy on Part B, the best response to nivolumab and ipilimumab was a partial response in 1 patient (6%) (unclassified/non-sarcomatoid), stable disease in 7 patients (44%), and progressive disease in 8 patients (50%). The median PFS in this cohort was 2.8 months.
Grade 3 Treatment-related adverse events were identified in 7 of 35 patients (20%) while on nivolumab monotherapy while grade 3-5 events were seen in 7 of 17 patients (41%) while receiving salvage nivolumab and ipilimumab, with one experiencing sudden death. Ongoing work will assess correlative studies including PD-L1 status, WES, and RNAseq.
The authors conclude that nivolumab monotherapy has limited activity in treatment naïve nccRCC. Among those who responded, most patients had sarcomatoid and/or unclassified tumors. Patients with low levels of PD-L1 expression did not have responses. Salvage treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab could be given in just over half of eligible patients but had limited ability to salvage non-responders. Thus, other treatment approaches are needed.
Presented By: Michael B. Atkins, MD, Deputy Director of the Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Scholl Professor and vice-chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washinton, DC
Written By: Christopher J.D. Wallis, MD, Ph.D., Urologic Oncology Fellow, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Contact: @WallisCJD on Twitter at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Virtual Annual Meeting #ASCO21, June, 4-8, 2021


