Dr. Shah and colleagues used data from the US Oncology Network of over 1,300 providers from over 480 sites across United States from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2020 (study period). The eligible study population included metastatic RCC patients who received ipilimumab + nivolumab (IO+IO), pembrolizumab + axitinib (IO+TKI), and axitinib or cabozantinib or pazopanib or sunitinib (TKIs monotherapy) in the first-line setting until September 30, 2020. Descriptive statistics were used for cohort characterization.
There were 3,756 metastatic RCC patients identified, of which 1,538 were eligible including 42% (n = 641) IO+IO, 18% (n = 279) IO+TKI, and 40% (n = 618) TKI monotherapy. The median age for the entire cohort was 67.1 years (range 25.0, 93.3), 70% (n = 1,076) were male, 70% (n = 1,081) were white, 38% (n = 587) had BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, and 79% (n = 1,208) had clear cell histology. Among entire cohort, 87% (n = 1,338) had intermediate/poor risk score as per IMDC risk model. There was a noted trend towards increased utilization of IO+IO and IO+TKI following their respective FDA approvals (IO+IO: April 2018, IO+TKI: April 2019):
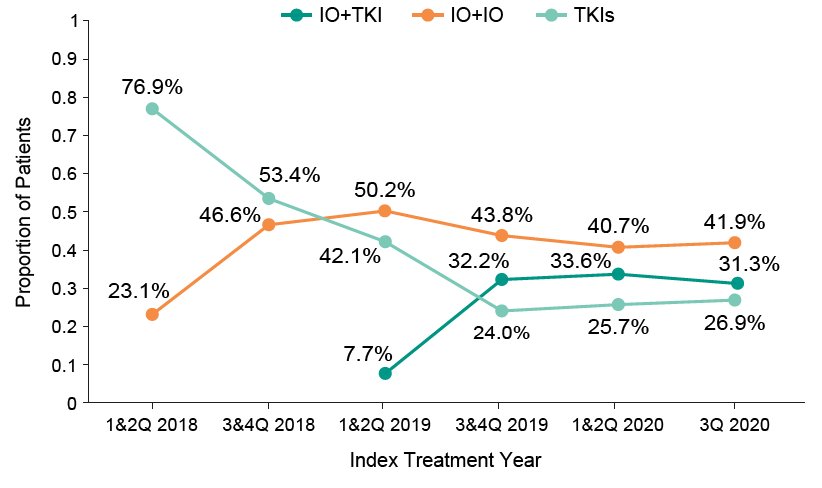
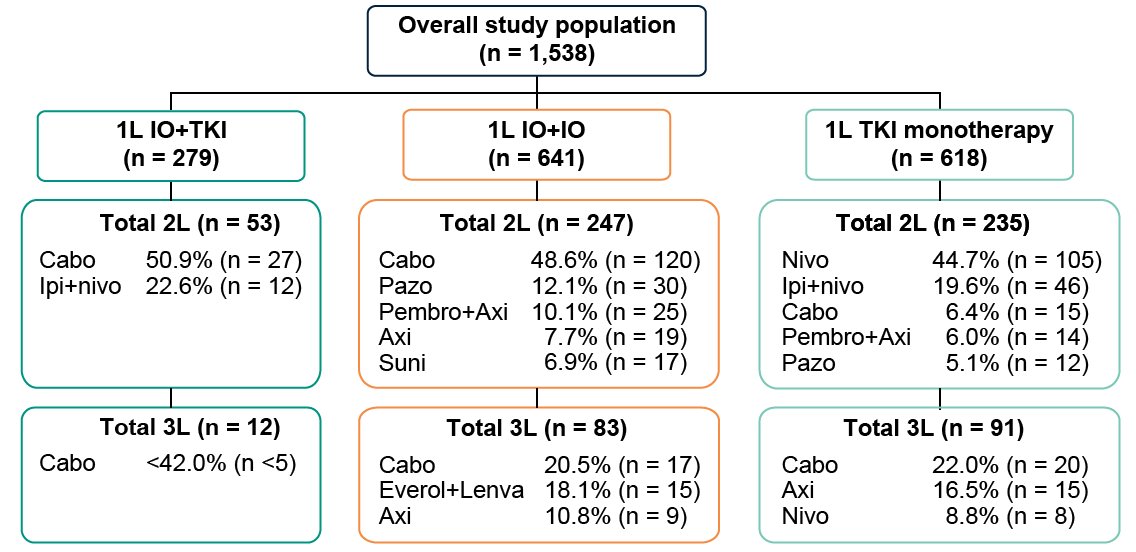
During the study period, overall, 35% (n=535), 12% (n=184), and 4% (n=62) of metastatic RCC patients received second-line, third-line, and fourth-line treatments, respectively. Cabozantinib (49%) and pazopanib (12%), cabozantinib (51%) and ipilimumab + nivolumab (23%), and nivolumab (45%) and ipilimumab + nivolumab (20%) were the most common second-line treatments in IO+IO, IO+TKI, and TKI monotherapy cohorts, respectively. As follows is the treatment sequence by line of treatment among metastatic RCC patients initiating first-line systemic treatments:
Dr. Shah concluded his presentation discussing real-world assessment of changing treatment patterns and sequence for patients with metastatic RCC in the first-line setting with the following concluding statements:
- Since approval of newer IO-based therapy, there was a noted substantial increase in uptake of IO-based combination treatments in first-line in the community setting in the US
- Second-line therapies were guided by therapies in first-line with most patient receiving a TKI if they received IO-based therapy in first-line and IO-based therapy if they received a TKI in the first-line
- A longer follow-up is needed to examine later lines of therapy and optimal sequencing after first-line therapies
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2022 International Kidney Cancer Symposium (IKCS) North America, November 4-5, Austin, Texas, USA


