(UroToday.com) The European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2021 annual meeting’s prostate cancer session included a presentation by Dr. Nuria Romero-Laorden discussing the final results of PRORADIUM, a study assessing the role of serum biomarkers of bone metabolism in mCRPC patients treated with radium-223. Radium-223 is a life-prolonging alpha-emitter bone targeted therapy for mCRPC patients with bone metastases.1 However, evidence on biomarkers that may help in patient selection are lacking. Total ALP appeared to be a potential marker of radium-223 effect in early studies.2 Other bone-related markers, such as bone-specific ALP, have also demonstrated their prognostic value in mCRPC patients with bone metastases.3,4 The hypothesis of this study was that bone-related markers may affect the clinical outcome of mCRPC patients treated with radium-223.
PRORADIUM (NCT022925702) is a prospective multicenter (35 Spanish centers) cohort study in mCRPC patients treated with radium-223. The study design of PRORADIUM is as follows:
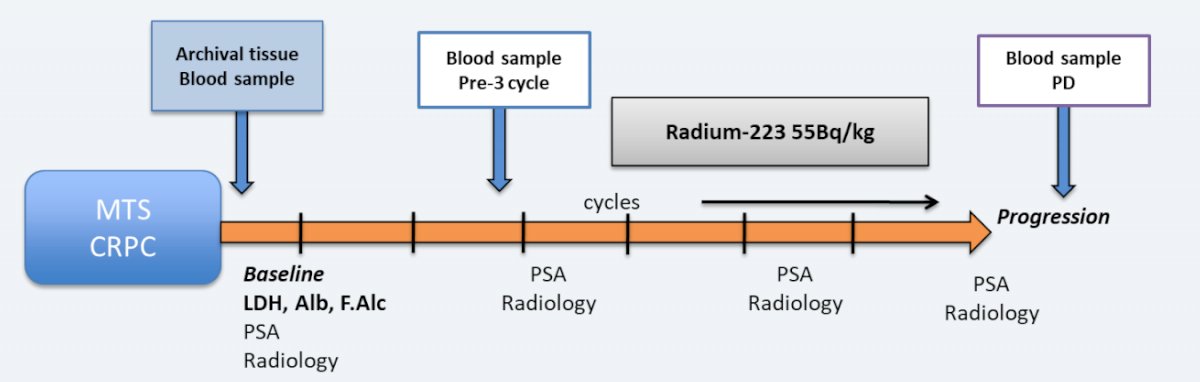
The primary aim was to assess the impact of baseline serum biomarkers of bone formation (bone-specific ALP and C-terminal of type 1 collagen propeptide) on overall survival. Secondary aims include the correlation of progression-free survival, time to PSA progression, and skeletal-related events free-survival with serum bone markers.
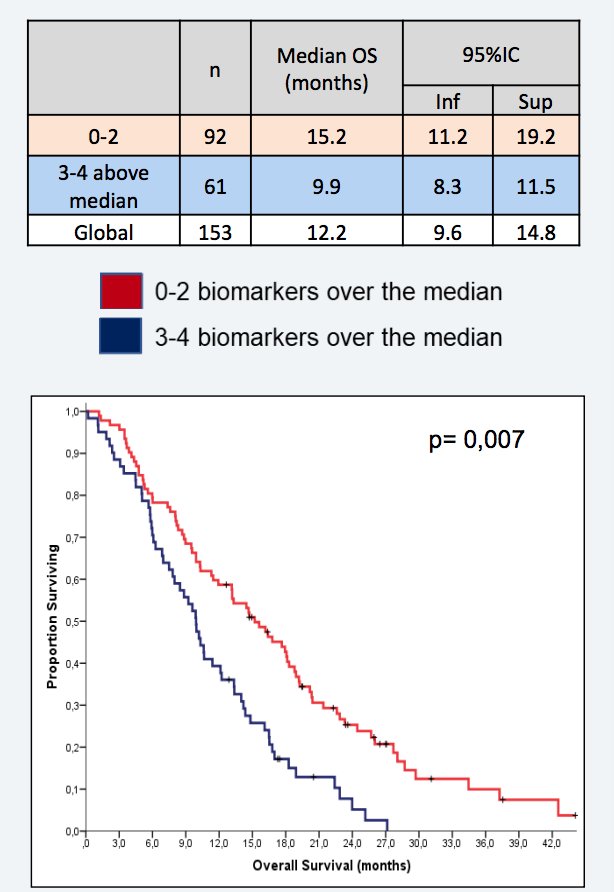
There were 169 patients included in this study and serum biomarkers were successfully analyzed in 153 patients. The median age was 74.4 years, 85.2% of patients had ECOG 0-1, and 57.5% of patients completed 5-6 cycles of radium-223. Total ALP was strongly correlated with shorter radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival (p < 0.001). Higher baseline levels of bone-specific ALP and C-terminal of type 1 collagen propeptide were associated to number of metastases in bone-scan (p = 0.002 and p = 0.001, respectively) and baseline pain (p = 0.003, p = 0.028, respectively). After a median follow-up of 31.1 months, 147 deaths were observed, with a median overall survival of 12.1 months (95% CI 9.5-14.7). Continuous value of bone-specific ALP and C-terminal of type 1 collagen propeptide correlated with a shorter time to PSA progression (bone-specific ALP: Q1 5.4m/Q4 3.3m, p=0.013; C-terminal of type 1 collagen propeptide: Q1 5.5m/Q4 3.6m, p = 0.011) and radiographic progression-free survival (bone-specific ALP: Q1 10.2m/Q4 5.4m, p=0.009; C-terminal of type 1 collagen propeptide: Q1 9.3m/Q4 6.9m, p =0.037), respectively. The elevation of 3-4 bone biomarkers over the median was significantly associated with worse overall survival (15.2 versus 9.9 months, HR 1.63, p = 0.007):
There were no associations found with skeletal-related event free-survival.
Dr. Romero-Laorden concluded this presentation of the PRORADIUM trial highlighting that baseline serum markers of bone formation may serve as biomarkers for prognosis in mCRPC patients treated with radium-223, however that validation analysis will be needed to confirm these results.
Presented by: Nuria Romero-Laorden, MD, PhD, Prostate Cancer Clinical Research Unit, Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), Madrid, Spain
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2021 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress 2021, Thursday, Sep 16, 2021 – Tuesday, Sep 21, 2021.
References:
- Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2013;369(3):213-223.
- Sartor O, Coleman RE, Nilsson S, et al. An exploratory analysis of alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, and prostate-specific antigen dynamics in the phase 3 ALSMPCA trial of radium-223. Ann Oncol. 2017 May 1;28(5):1090-1097.
- Fizazi K, Massard C, Smith M, et al. Bone-related parameters are the main prognostic factors for overall survival in men with bone metastases from castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2015 Jul;68(1):42-50.
- Lara Jr PN, Ely B, Quinn DI, et al. Serum biomarkers of bone metabolism in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients with skeletal metastases: Results from SWOG 0421. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 Apr;106(4)dju013.


