Prior work by the primary author (Beuselinck et al. CCR 2015 and Acta Oncologia 2017) have demonstrated that within ccRCC there are 4 molecular subtypes (1-4). ccRCC type 2 had a high angiogenic gene signature, long PFS and good response to TKI – likely corresponding to “good risk disease”. ccRCC 1 and 4, however, had intermediate and poor PFS and poor response to TKI’s.
In this study, the authors aim to study the underlying biologic mechanisms. They analyzed their ccRCC databank of patients and correlated the IMDC prognostic score at start of systemic therapy with mRNA-expression of genes involved in angiogenesis (HIF1A/2A, VEGFA, VEGFR1/2/3) and in the immunosuppressive microenvironment (PD1, PDL1/2, LAG3, CD8A, CD3G, IFNG, CXCL13) and with the molecular ccrcc1-4 classification of the primary tumor.
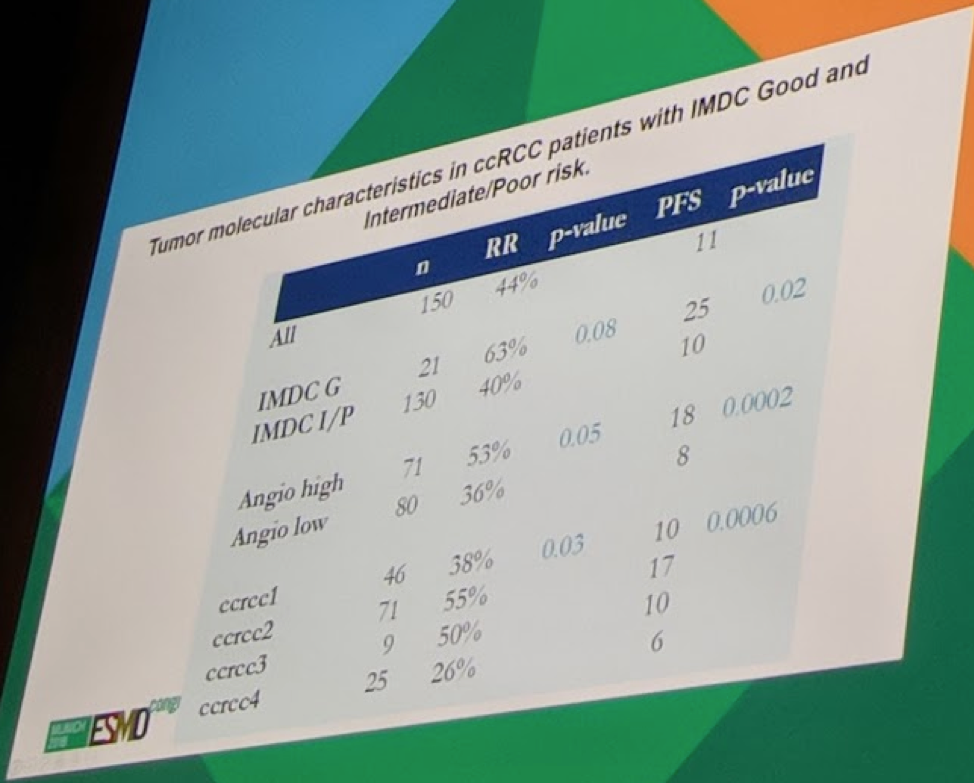
They had 162 patients in the study, of which 14% were IMDC good-risk (G-risk), 65% intermediate (I-risk) and 21% poor risk (P-risk).
The majority of G-risk pts (77%) had ccrcc2-tumors, which correlates well to the high PFS and response to TKIs. Good-risk patients were less likely to have ccrcc1- (14%) and ccrcc4-tumors (0%).
In I/P-risk patients, ccrcc2-tumors were less frequent (41%), and ccrcc1- (34%) and ccrcc4-tumors (20%) more frequent – again consistent with prior work.
mRNA expression of HIF2A, VEGFR1, -2 and -3 (angiogenesis pathway) was higher in G-risk pts compared to I/P-risk pts, correlating with a higher angiogenic profile and response to TKIs Identical expression of immune-related genes was found across all IMDC subgroups.
Presented by: Beuselinck Benoit, Prof. Dr. medical Oncologist, Leuven, Belgium
Written by: Thenappan Chandrasekar, MD, Clinical Instructor, Thomas Jefferson University, twitter: @tchandra_uromd, @TjuUrology at the 2018 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress (#ESMO18), October 19-23, 2018, Munich Germany


