Patients who had undergone radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy between May 2014 and September 2020 were evaluated retrospectively. Demographical, clinical, and pathological data of the patients were reviewed, and scores of Briganti 2012 and Partin nomograms were calculated for all patients. The 2018 Briganti nomogram scores were calculated only for patients with MRI targeted prostate biopsies and multiparametric prostate MRIs prior to radical prostatectomy (n=34). For Briganti 2012 and Partin nomograms, 5% and above scores were accepted as positive. For the 2018 Briganti nomogram, the cutoff value was 7%. These scores were compared with the lymph node status of Ga-68 PSMA PET reports.
Among 99 patients, the median patient age was 65 (range: 48-75) years and the median PSA value was 8 (range: 2.5-99) ng/ml. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) scores of prostate biopsies were 1 in 9 patients, 2 in 29 patients, 3 in 23 patients, 4 in 23 patients, and 5 in 15 patients. According to D’Amico risk classification, 6 patients were at low, 54 were at intermediate, 39 were at high-risk groups. A final pathology, pathological T2 and locally advanced prostate cancer were present in 41 and 58 patients, respectively. The number of patients with ISUP scores of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 was 5, 35, 29, 9, and 21, respectively at final pathology. The median lymph node yield was 17 (1-47) and 15 (10.4%) patients had LNI (11 at high, 4 at intermediate risk groups). Rates of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for Briganti 2012, the 2018 Briganti, Partin nomograms, and Ga-68 PSMA PET are as follows: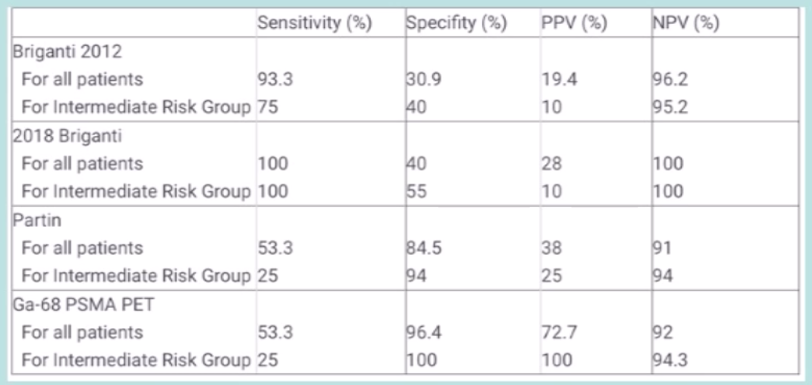
Unnecessary lymphadenectomy would have been avoided in 55/58 (94.8%) false-positive patients of Briganti 2012, 17/18(94.4%) false-positive patients of 2018 Briganti, 12/13 (92.3%) false-positive patients of Partin nomograms, if Ga-68 PSMA PET was used to predict lymph node status.
Dr. Kordan concluded his presentation with the following take-home messages:
- Despite lower sensitivity rates, Ga-68 PSMA PET had the highest rates of specificity and positive predictive value (100% for the intermediate-risk group)
- With supporting data from larger series, using Ga-68 PSMA PET as a lymph node invasive prediction tool instead of nomograms could avoid unnecessary lymphadenectomies during radical prostatectomy
Presented By: Yakup Kordan, MD, Koc University School of Medicine, Department of Urology, Istanbul, Turkey
Written By: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2021 European Association of Urology, EAU 2021- Virtual Meeting, July 8-12, 2021.
References:
- Briganti A, Larcher A, Abdollah F, et al. Updated nomogram predicting lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer undergoing extended pelvic lymph node dissection: The essential importance of percentage of positive cores. Eur Urol. 2012 Mar;61(3):480-487.
- Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Zaffuto E, et al. Development and internal validation of a novel model to identify the candidates for extended pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer. Eur Urol 2017;72(4):632-640.


