(UroToday.com) The 2021 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Hybrid Annual Meeting’s included a session on biomarkers and salvage radiotherapy and discussion by Dr. David J. Konieczkowski regarding the impact of AR-V7 and other androgen receptor splice variant expression on outcomes of post-prostatectomy salvage therapy.
The benefit of ADT in post-radical prostatectomy salvage therapy is now established, yet patient selection is critical. Clinicopathologic features (ie. PSA, etc) is likely important, but can molecular features also inform decision-making? Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer is important and is highlighted in the following figure:
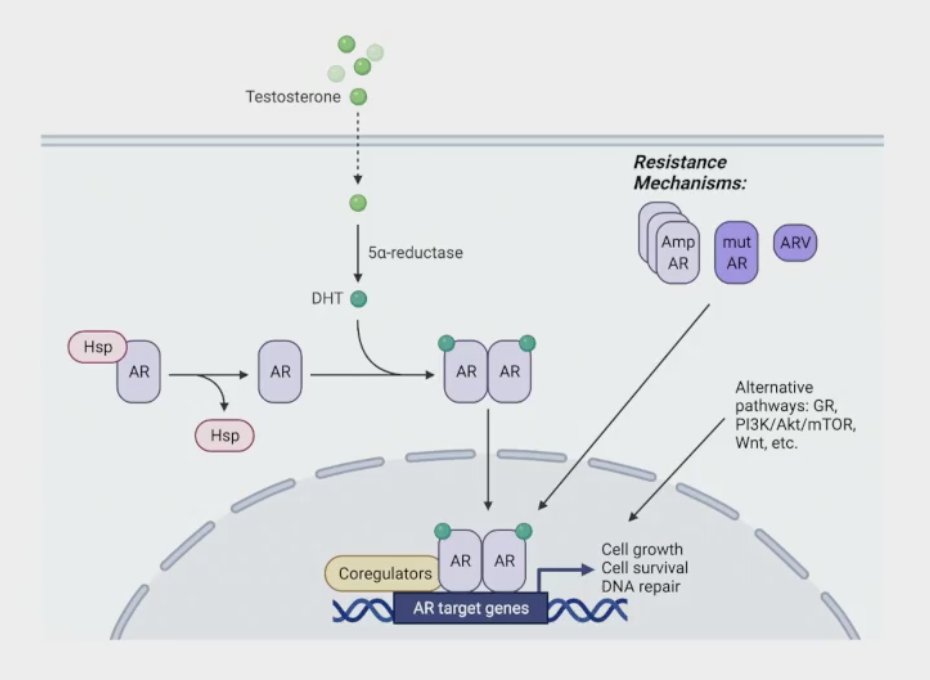
AR-V7 positivity confers ADT resistance and has been established as a prognostic factor in mCRPC and mCSPC, but the effect of AR-V7 status in localized disease remains to be further elucidated. AR directly transactivates DNA damage repair genes, and AR-Vs may also mediate DNA repair in vitro. Thus, could AR-Vs also modulate response to radiotherapy in patients?
Dr. Konieczkowski’s group (unpublished data) assessed 46 patients that underwent radical prostatectomy between 1993-2011 who ultimately underwent salvage radiotherapy. The median interval from surgery to salvage radiotherapy start was 25.7 months (range: 4.1 – 139.5), with a median PSA at salvage radiotherapy of 0.57 ng/mL. The median salvage radiotherapy dose was 64.8 Gy, 37% of patients received nodal radiotherapy at the time of salvage therapy, with 100% of patients receiving concurrent ADT. The median follow-up after salvage therapy was 33.8 months. Among these patients, comprehensive AR-V interrogation by ultra-deep sequencing was undertaken. For FFPE samples, RNA extraction was performed, followed by library preparation and a custom bait library of 3,127 primers tiling the entire AR transcript. Subsequently ultra-deep sequencing was performed, with a mean depth of coverage of >5,000x, thus providing detailed analysis of the AR transcriptome. The splice variant landscape from this analysis suggested that 76% of tissues harbored an AR-V splice variant of some sort:

These AR-V splice variants were then correlated to outcomes after salvage therapy, mutations associated with early failure, late failure, and no failure:

In their analysis, AR-V7 expression is associated with worse outcomes after salvage radiotherapy + ADT, with ARV7 positive patients having a median survival of 10.9 months versus 73.4 months for patients with ARV7 negative mutations (HR 5.234, 95% CI 1.62-16.87):

Interestingly, there was no association between months from prostatectomy and proportion free from salvage radiotherapy (p = 0.37).
Dr. Konieczkowski concluded his presentation of the impact of AR-V7 and other androgen receptor splice variant expression on outcomes of patients being considered for salvage radiotherapy with the following take-home messages:
- Similar to metastatic prostate cancer, androgen receptor splice variants are detectable in primary prostate cancer at the time or prostatectomy
- AR-V7 expression in primary prostate cancer at the time of prostatectomy is associated with inferior outcomes following subsequent salvage radiotherapy + ADT
- Ongoing exome- and expression-based analyses will examine other genomic correlates of AR-V7 status and response to treatment.
Presented by: David J. Konieczkowski, MD, PhD, The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2021 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Hybrid Annual Meeting, Sat, Oct 23 – Wed, Oct 27, 2021.


