(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) cancers symposium held in San Francisco, CA was host to a prostate cancer trials in progress poster session. Dr. Kristine Lacuna presented the framework for the SBRT-AMICO trial, a phase 2 single-arm study testing stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), adenosine signaling modulation, and immune checkpoint inhibition for men with oligometastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC).
Dr. Lacuna noted that the standard of care for newly diagnosed mHSPC remains doublet therapy (ADT + an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor [ARPI] or docetaxel) or triplet therapy (ADT+ APRI + docetaxel). However, oligometastatic mHSPC represents a potentially unique disease state that may derive benefit from local therapy. Among patients with metachronous, oligometastatic mHSPC, there is evidence from the phase 2 STOMP and ORIOLE trials,1,2 of a benefit for metastasis-directed therapy. Further investigation is needed to determine the optimal approach for oligometastatic mHSPC, especially in the era of PSMA-PET/CT.
Radiotherapy has been demonstrated to increase the number of suppressive immune cells in the irradiated tumor and induce the highly suppressive adenosine pathway, via the following:
- In response to radiotherapy, ATP is released from tumor cells
- ATP is rapidly metabolized by ectonucleases CD39 and CD73
- Within the tumor microenvironment, free adenosine binds to A2AR and A2BR to promote immunosuppression, which blunts the anti-tumor immune response
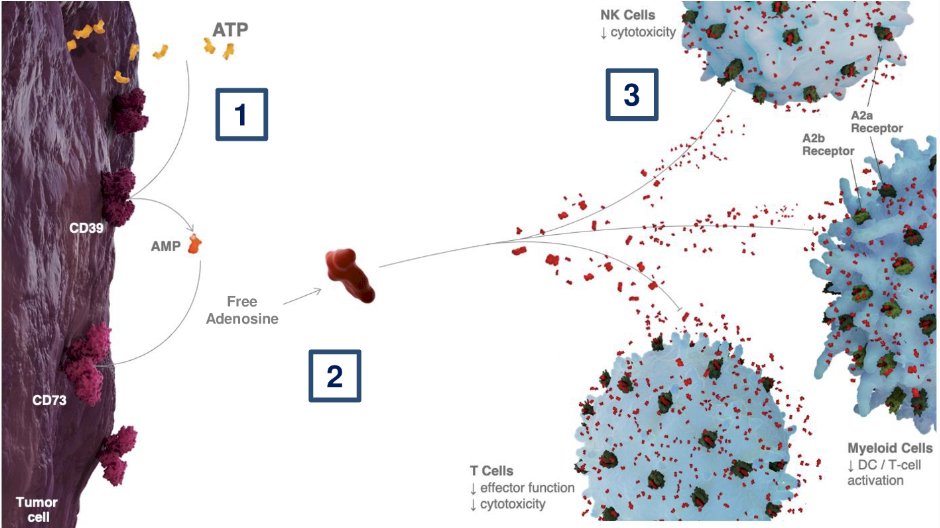
Thus, the adenosine signaling pathway represents an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in the context of metastasis-directed radiotherapy. Furthermore, adenosine signaling increases PD-1 expression, further blunting anti-tumor immune response. In pre-clinical models, the addition of tumor irradiation to adenosine signaling modulators and an immune checkpoint inhibitor have been shown to improve tumor control.3
As such, the investigators hypothesized that SBRT plus adenosine signaling modulators (adenosine receptor A2AR/A2BR inhibitor: AB928; CD73 inhibitor: AB680) combined with ICI (anti-PD-1: AB122) will improve biochemical recurrence-free survival compared to SBRT alone.
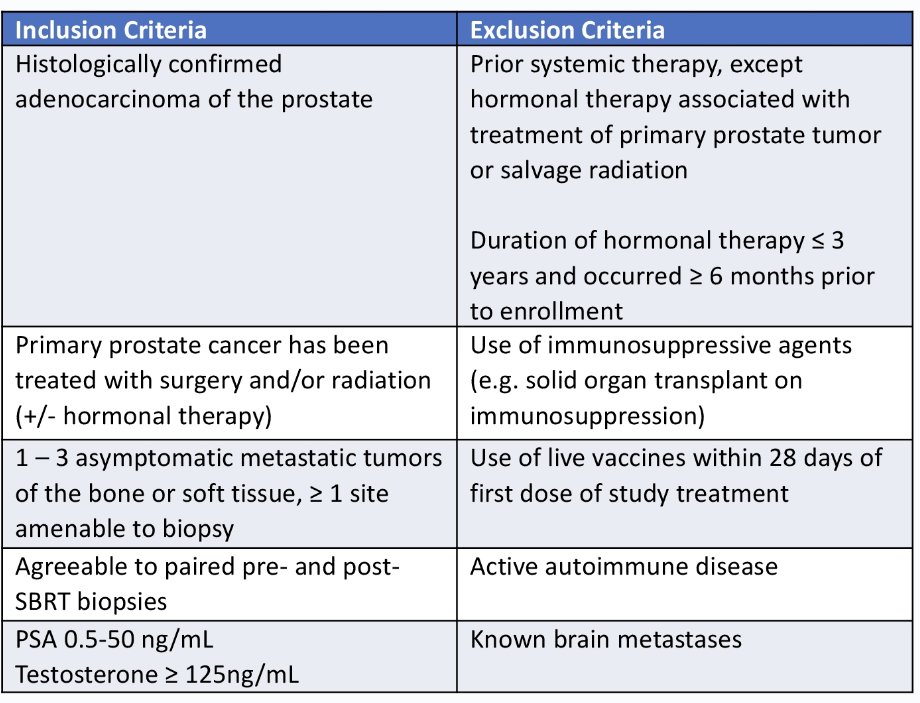
The key study eligibility criteria are summarized below:
This is a single-arm, investigator-initiated phase 2 trial of a CD73 inhibitor (AB680), A2AR/A2BR inhibitor (AB928), anti-PD-1 (AB122) with metastasis-directed therapy using SBRT for oligometastatic mHSPC.
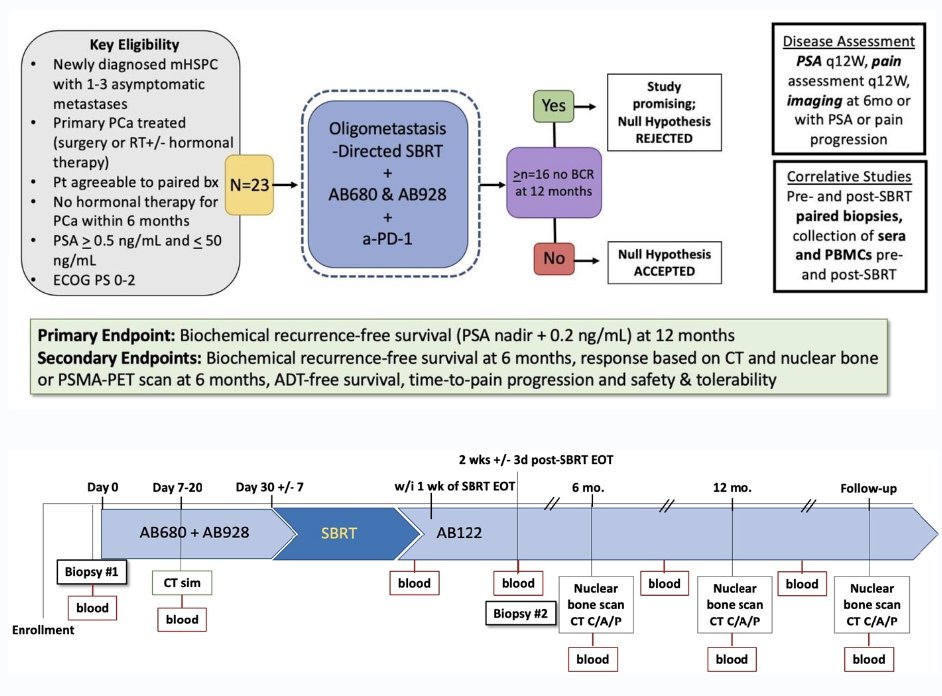
With regards to treatment overview:
- All patients will receive AB680, AB928, AB122 plus SBRT
- Week 1: Start adenosine signaling modulators AB680 100 mg IV q2 weeks + AB928 150 mg PO daily
- Week 4 (+/- 1 week): Start SBRT (1-5 fractions depending on size/location of metastasis per AAPM Task Group 101)
- Within 1 week of completing SBRT: Start anti-PD-1 with AB122 240 mg IV q2 weeks
With regards to treatment duration, treatment may continue for up to 32 months, or until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity/adverse events, withdrawal of consent, or illness/changes in condition deemed unacceptable for further treatment.
The primary study objective was biochemical recurrence-free survival, defined as PSA >0.2 ng/mL above post-SBRT nadir. Secondary outcomes included:
- Biochemical recurrence-free survival at 6 months
- CT, nuclear bone scan, or PSMA PET response at 6 months
- ADT-free survival
- Time-to-pain progression
- Safety and tolerability
The statistical plan is as follows:
- Kaplan-Meier method will be used to analyze biochemical recurrence-free survival
- Biochemical recurrence-free survival will be reported at the median and at 12 months to evaluate potential benefit of treatment.
- Using a 1-sided alpha of 0.1 and power of 0.8, the design calls for 23 patients to demonstrate improvement in biochemical recurrence free survival of 0.5 (historical control, null hypothesis) to 0.71 (alternative) at 12 months.
- Biochemical recurrence-free survival will be compared to available historical data examining SBRT alone for PSMA-PET detected oligometastatic mHSPC.
The planned translation research is summarized below:

The study opened for accrual in July 2023.
Presented by: Kristine Peregrino Lacuna, MD, Department of Medicine, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, January 25th – January 27th, 2024
References:
- Ost P, Reynders D, Decaestecker K, et al. Surveillance of metastasis-directed therapy for oligometastatic cancer recurrence: A prospective, randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb 10;36(5):446-453.
- Phillips R, Shi WY, Deek M, et al. Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2020 Mar 26;6(5):650-659.
- Allard B, Pommey S, Smyth MJ, Stagg J. Targeting CD73 enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(20):5626-35.


