(UroToday.com) On the second day of the American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Genitourinary Cancer Symposium 2023 focussing on urothelial cancer, the Oral Abstract Session B included a presentation from Dr. Andrea Necchi discussed results of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with high-risk non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (HR NMIBC) unresponsive to bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) in the context of cohort B of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-057 trial.
In patients with HR-NMIBC, guidelines recommend treatment with BCG. While most patients will initially respond, those who do not respond or who relapse within 12 months have poor prognosis. In this space, radical cystectomy (RC) is a treatment option though it carries significant toxicity. As such, there is an unmet need for alternative approach.
The single-arm, multicohort phase 2 KEYNOTE-057 trial (NCT02625961) was designed to investigate the safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab monotherapy for patients with BCG-unresponsive HR NMIBC (per FDA) who were ineligible or declined to undergo RC.

Initial results from cohort A (carcinoma in situ [CIS] with or without papillary tumors) showed a complete clinical response rate of 41% at 3 months and led to the approval of pembrolizumab monotherapy for this indication in the United States. In this presentation, Dr. Necchi provided updated results from cohort B (papillary tumors without CIS), a disease space where there are relatively few treatment options.
In this trial, the authors enrolled adult patients (aged ≥18 years) with BCG-unresponsive HR NMIBC with papillary tumors only (high-grade Ta or any-grade T1) at baseline and ECOG PS 0-2.
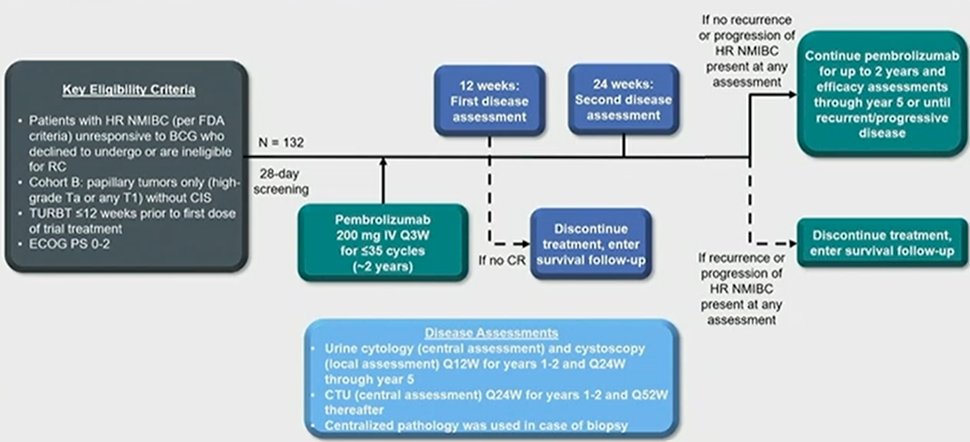
Enrolled patients received pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (~2 years). Patients underwent cancer assessments at 12 weeks and then every 12 weeks thereafter if no recurrent HR NMIBC or progression was observed. Patients further underwent CT urography every 24 weeks. In cohort B, the primary endpoints were 12-month disease-free survival (DFS) rate of HR NMIBC as assessed by central pathology/radiology review and safety, assuming a 12-mo DFS of >20% for HR NMIBC. Additionally, the authors considered further secondary efficacy endpoints including a 12-month DFS rate of any disease; progression-free survival (PFS) to worsening of grade, stage, or death; PFS to muscle invasion, metastasis, or death; and overall survival (OS).
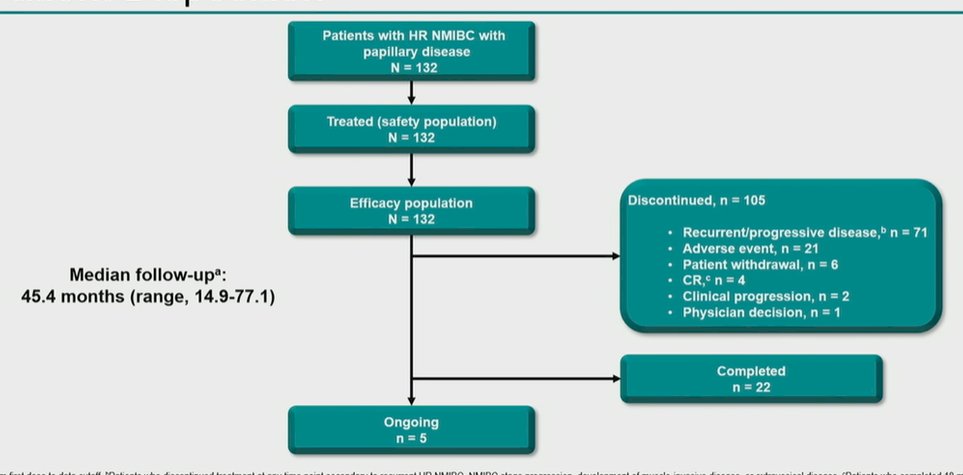
In cohort B of KEYNOTE-057, 132 patients received pembrolizumab for a median of 9.5 cycles (range, 1.0-35.0). In this cohort, the median age was 72 years (range, 37-87). In this cohort, 57 patients (43.2%) had T1 disease and all patients (100%) had urothelial histology. Among the 132 patients, 104 (78.8%) were male. Prior to enrollment, patients received a median of 10 (range, 6-33) prior BCG instillations.
Over a median follow-up of 45.4 months (range, 14.9-77.1), the authors found that 105 patients discontinued therapy of whom the majority (71) had disease progression while 22 patients completed therapy and 5 were receiving ongoing treatment.
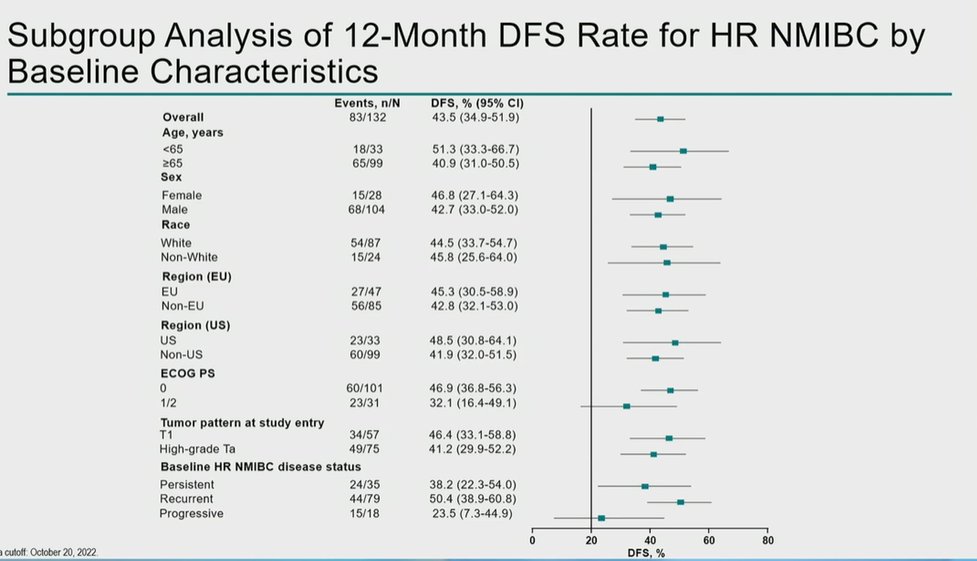
In terms of disease free survival from HR-NMIBC, 83 patients (63%) eventually had recurrence, progression or death. At 12, 24, and 36 month landmark analyses, the disease free survival was 43.5% (95% CI 35-52%), 34.9% (95% CI 26-43%), and 34.9% (95% CI 26-43%), respectively.
Perhaps not unexpected, disease-free survival for any disease was somewhat lower with rates at 12, 24, and 36 month landmark analyses of 41.7% (95% CI 33-50%), 33.0% (95% CI 25-42%), and 33.0% (95% CI 25-42%), respectively.
Importantly, this DFS benefit was seen across nearly all subgroups defined based on clinical, demographic, and pathologic characteristics, with the notable exception of the progressive HR NMIBC subset.
Considering progression-free survival, Dr. Necchi noted 88.2% (95% CI 80-93%) rates of progression-free survival both to worsening of grade, stage, or death and to invasive or metastatic disease, or death. The median overall survival was not reached with only 27 deaths in the cohort so far. 1 year overall survival was 96.2% (95% CI 91-98%).
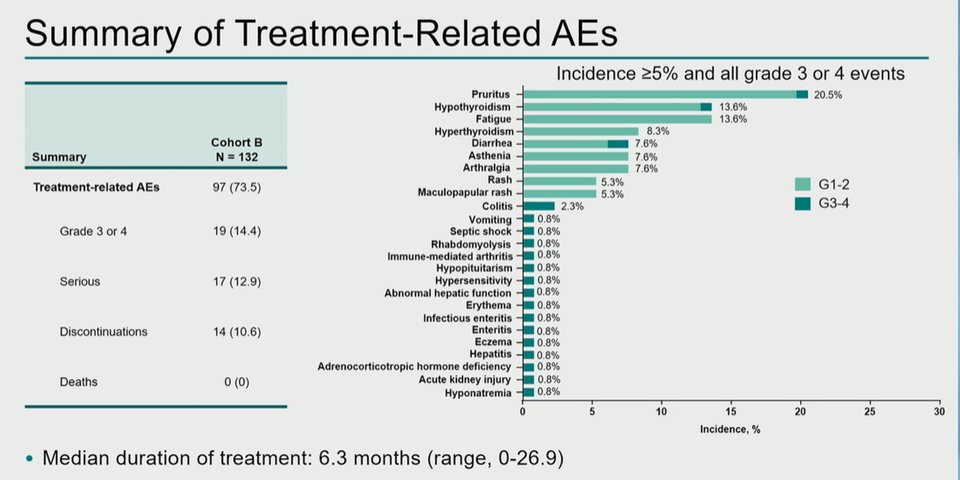
Following cessation of pembrolizumab, thirty-one patients (23.5%) underwent RC. Treatment-related adverse events occurred in 97 patients (73.5%). Of these, 19 (14.4%) had a grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse event and 14 pts (10.6%) discontinued due to a treatment-related adverse events. However, no deaths from treatment-related adverse events occurred. Immune-related and infusion reactions were uncommon.
Dr. Necchi further noted that patients’ quality of life was relatively well preserved during therapy, as measured with changes in FACT-G total score and FACT-BI total score.
Thus, Dr. Necchi concluded that pembrolizumab monotherapy showed notable antitumor activity in patients with BCG-unresponsive non-CIS papillary HR NMIBC after nearly four years of follow-up. Toxicity was manageable and consistent with that in cohort A, with no new safety signals. As a result, these results suggest patients with non-CIS papillary HR NMIBC unresponsive to BCG who decline or are ineligible to undergo RC may also benefit from pembrolizumab monotherapy.
Presented by: Andrea Necchi, MD; Vita-Salute San Raffaele University; Department of Medical Oncology, IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital and Scientific Institute
Written by: Christopher J.D. Wallis, University of Toronto Twitter: @WallisCJD during the 2023 Genitourinary (GU) American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, San Francisco, Thurs, Feb 16 – Sat, Feb 18, 2023.
Related Content:
Results from Cohort B of the Phase 2 KEYNOTE-057 Trial, Pembrolizumab Monotherapy for Patients with High-Risk Non–muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Unresponsive to BCG - Andrea Necchi


