Approximately 70% of RCC have clear cell histology. Non-clear cell histology comprises the remaining heterogenous histologic subtypes, and patients with non-clear cell aRCC generally have a poor prognosis, with no definitive established treatment.
The phase 3b/4 Checkmate 374 trial was conducted to confirm safety and efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy 240 mg every two weeks as a flat dose in patients with aRCC, including patients with non-clear cell RCC. Initial safety results demonstrated that Nivolumab at 240mg every two weeks had a consistent safety profile across patients with clear cell and non-clear cell advanced RCC. This dosage was approved by the FDA and EMAin April 2018.
In this poster, the authors report safety and efficacy data in patients with non-clear cell RCC from Checkmate 374. This was an open-label, phase 3b/4 trial of nivolumab monotherapy in patients with aRCC (Clinical trial information: NCT02596035) (Figure 1 shows study design). The primary endpoint was the incidence of high grade (3-5) immune-mediated adverse events.
The study enrolled 44 patients with non clear cell RCC (Table 1). At the data cutoff, all patients had discontinued treatment, with disease progression being the most common reason for treatment discontinuation (73%). Median follow-up was 11.1 months.
Figure 1- Study design:
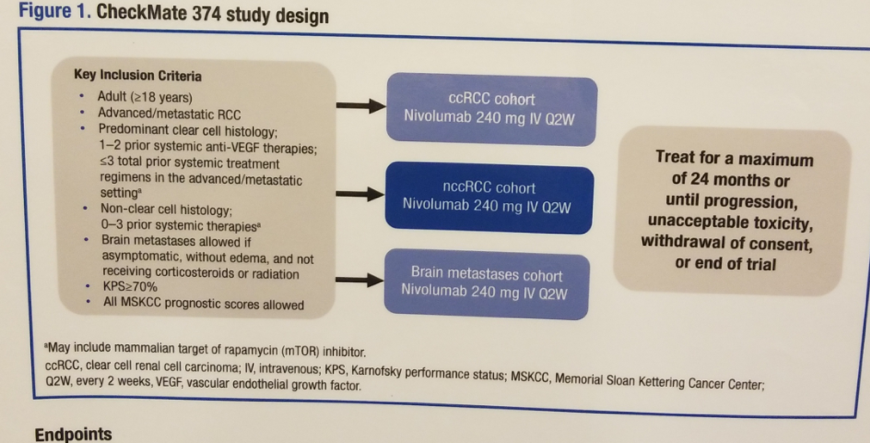
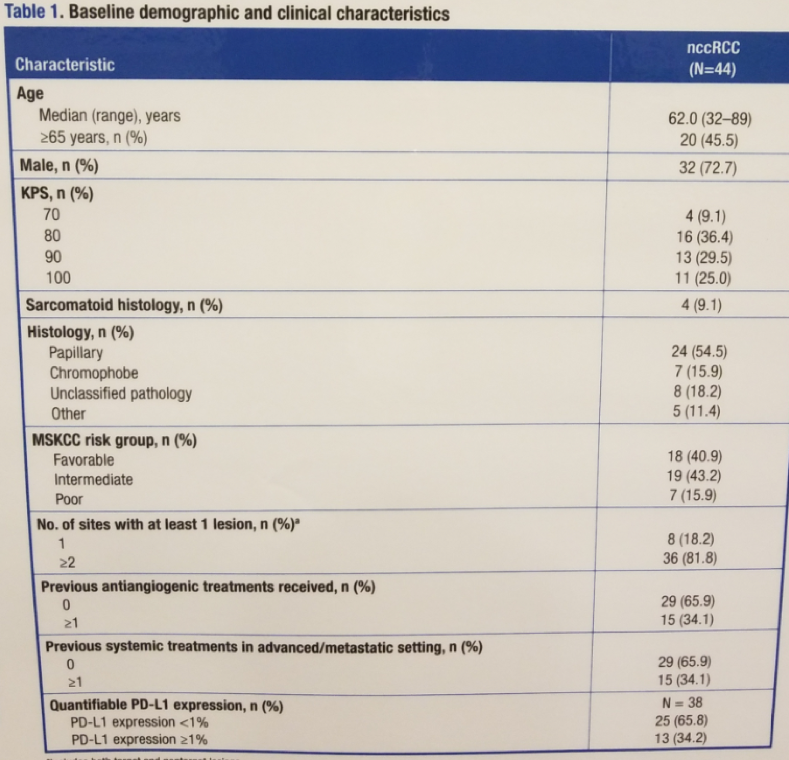
Table 2 – Treatment-related immune-mediated adverse events:
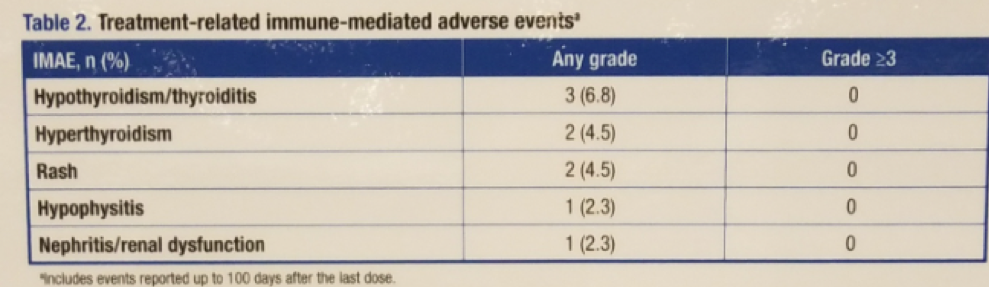
Figure 2 – Overall survival in all treated patients and by tumor PD-L1 expression:
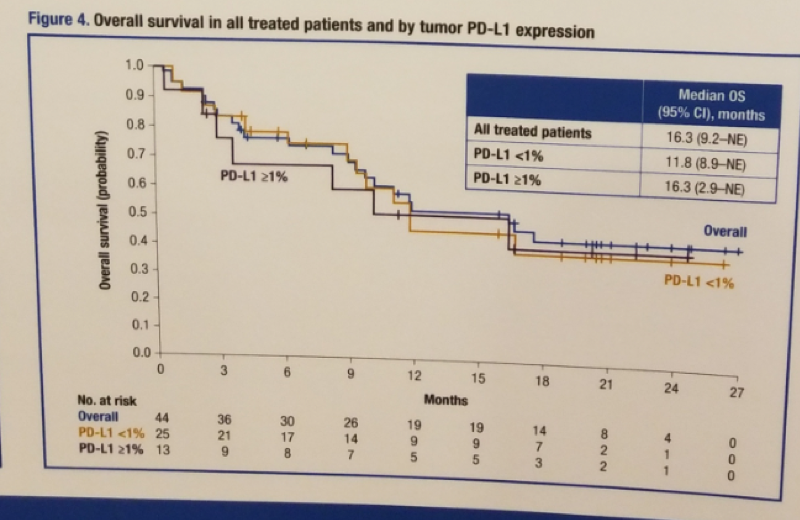
In conclusion, the safety profile of the flat dose of nivolumab is consistent with that previously reported in patients with aRCC and no new safety signals were identified. Clinically meaningful survival and antitumor activity were observed in the first prospective study of nivolumab monotherapy in non-clear cell RCC. Furthermore, clinically meaningful survival results were observed in patients regardless of their tumor PD-1 expression at baseline. These reported results establish nivolumab monotherapy as a treatment option for patients with non-clear cell RCC.
Presented by: Nicholas Vogelzang, MD, FASCO, FACP, Comprehensive Cancer Centers of Nevada, Las Vegas, Nevada
Written by: Hanan Goldberg, MD, Urologic Oncology Fellow (SUO), University of Toronto, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, @GoldbergHanan at the 2019 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary Cancers Symposium, (ASCO GU) #GU19, February 14-16, 2019 - San Francisco, CA


