
Patient randomization resulted in treatment arms that were evenly matched for age, PSA, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG), Gleason score, treatment to date, and disease sites. The addition of palbociclib to ADT with Lupron® and bicalutamide did not improve the primary outcome of PSA < 4 ng/mL, and was also not associated with differences in complete PSA response or radiologic response.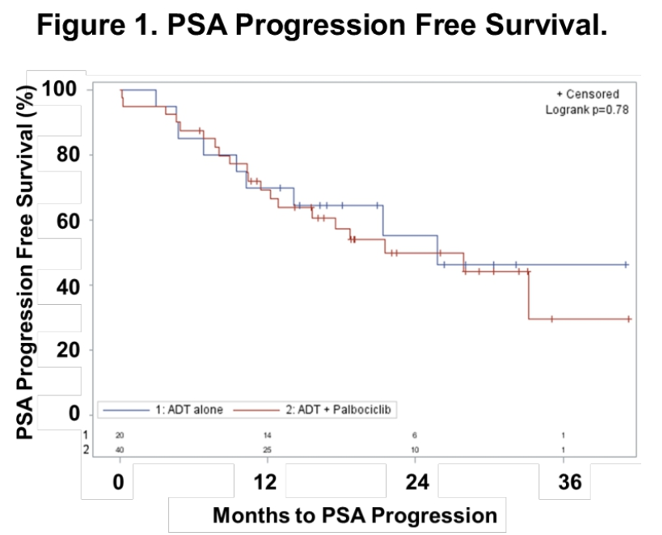
Regarding correlative studies, the authors found that pretreatment CTC counts ≥ 2/mL were associated with decreased rates of PSA response and progression-free survival.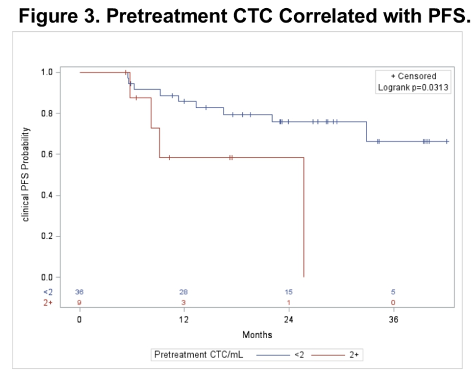

Mutations in TP53, PIK3, and gain of chromosome 8q were significantly associated with time to PSA progression.
In conclusion, no difference in PSA or clinical response was observed in this biomarker stratified randomized Phase II trial of the addition of palbociclib ADT with bicalutamide. Correlative analyses showed that higher CTC levels and certain genomic alterations associated with prostate cancer were enriched for decreased progression-free survival. Further study of CDK4/6 inhibitors with more recent androgen receptor inhibitors may still be warranted.
Presented by: Phillip Lee Palmbos, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Written by: Alok Tewari, MD, PhD, Medical Oncology Fellow at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, at the 2020 American Society of Clinical Oncology Virtual Annual Meeting (#ASCO20), May 29th-May 31st, 2020


