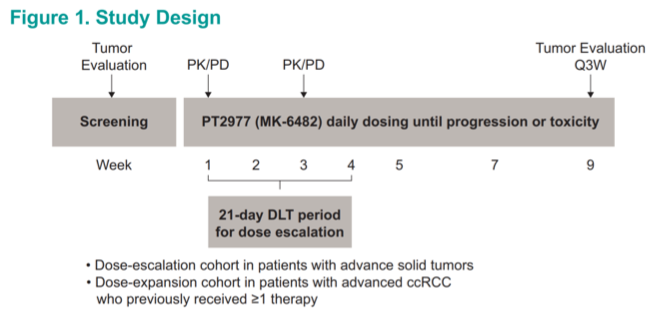
Barcelona, Spain (UroToday.com) Hypoxia inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) is known to mediate von Hippel-Lindau (VLH) associated oncogenesis. Deficiency of the VHL tumor suppressor leads to HIF-2α stabilization and intracellular accumulation, thereby promoting the formation of heterodimers with HIF-1β. These heterodimer acts as a key transcription factor for genes which promote tumorigenesis, such as VEGFA, thereby fueling oncogenesis.1 PT2977 (also known as MK-6482) is a small molecule inhibitor of HIF-2α which acts to block formation of the active heterodimer. Based upon promising preclinical data,2 investigators launched a clinical development program for PT2977. Eric Jonasch, MD, reported on the renal cell carcinoma dose expansion cohort of a phase I/II trial investigating the safety and efficacy of PT2977 in advanced solid tumors at ESMO 2019. A regimen of 120mg daily was selected on the basis of the dose escalation phase.
A total of 55 patients with treatment refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma were treated on protocol in the dose expansion phase. At a median age of 62 and an 80% male predominance, the cohort is fairly representative of the general mRCC population. Most notably, the majority (62%) had already received ≥3 lines of prior systemic therapy at the time of enrollment, representing a very heavily pretreated population with limited therapeutic options.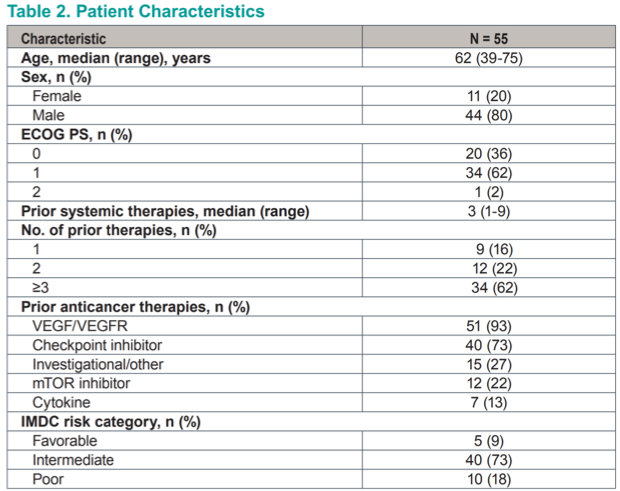
At the time of data cutoff, 71% of patients had discontinued therapy, mostly owing to adverse events (55%); one patient (2%) passed away on study. Treatment is ongoing in 16 (29%) patients. The most common all-grade adverse events were anemia, fatigue, dyspnea, nausea, and cough. Grade 3 anemia occurred in 26% of patients and grade 3 hypoxia in 15%; only 2 patients experienced grade 4 toxicities. Anemia was reasonably wel-managed by the administration of erythropoietin. Hypoxia was thought to be due to pulmonary vasocontriction in response to HIF-2α inhibition. It was managed effectively with supplemental oxygen and resolved with stopping the drug.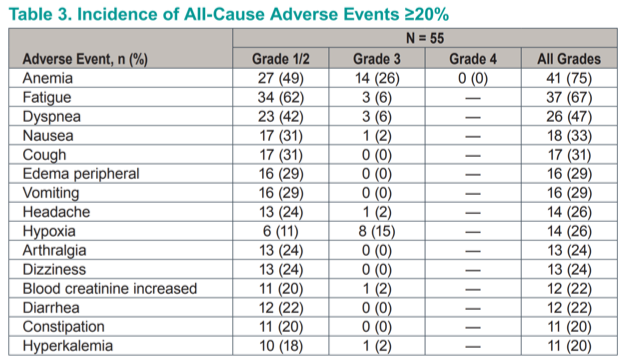
Efficacy endpoints in this heavily pretreated population were encouraging, with an objective response rate of 24% (all partial responses). A further 56% of patients achieved stable disease as their best response for a cumulative disease control rate of 80%. This toxicity profile compares very favorably to the known toxicity profiles of standard-of-care cabozantanib or everolimus plus lenvatinib.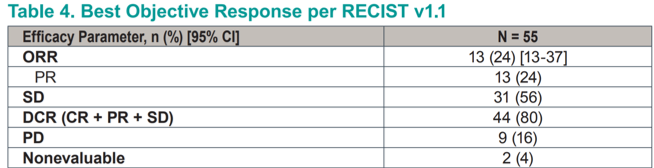
A total of 69% of patients achieved some degree of tumor shrinkage, and only 16% experienced frank progression.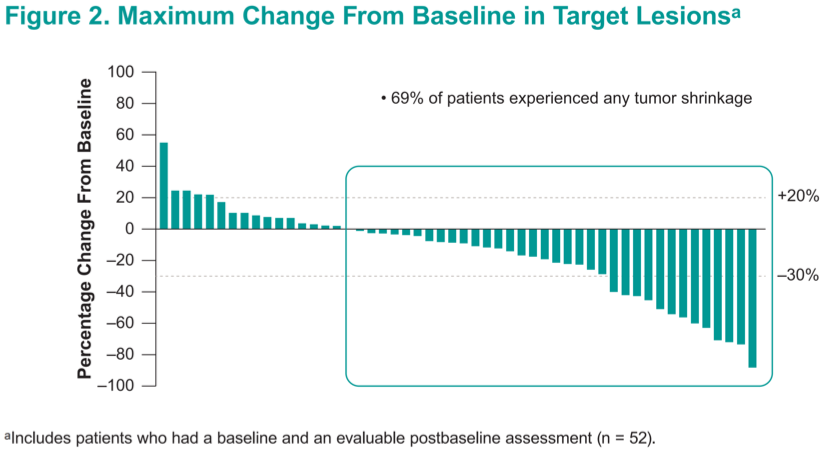
While follow-up data are immature, responses were generally ongoing after 50 weeks on treatment, and several patients with tumor shrinkage that did not rise to the level of an objective response continued to have disease control up to 70 weeks on therapy. 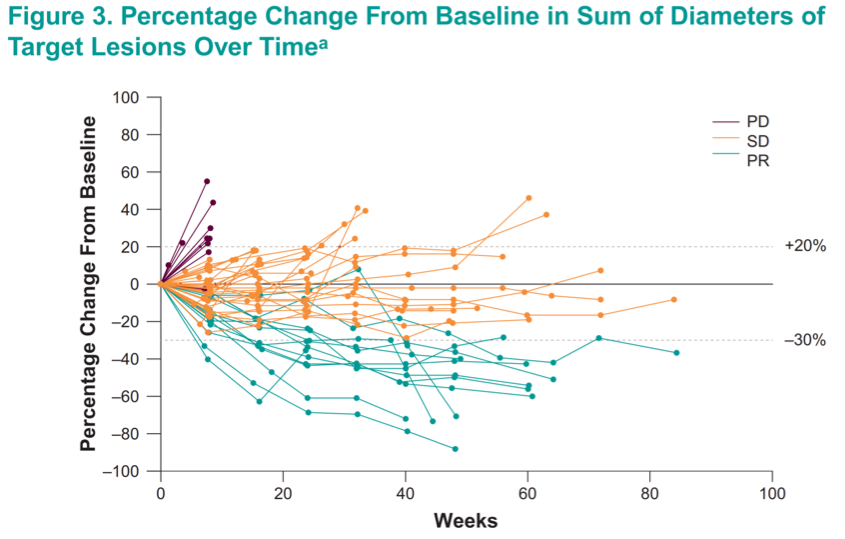
Interestingly, while responses were generally first noted within 20 weeks, several late responses were recorded – even after 40 weeks on treatment. 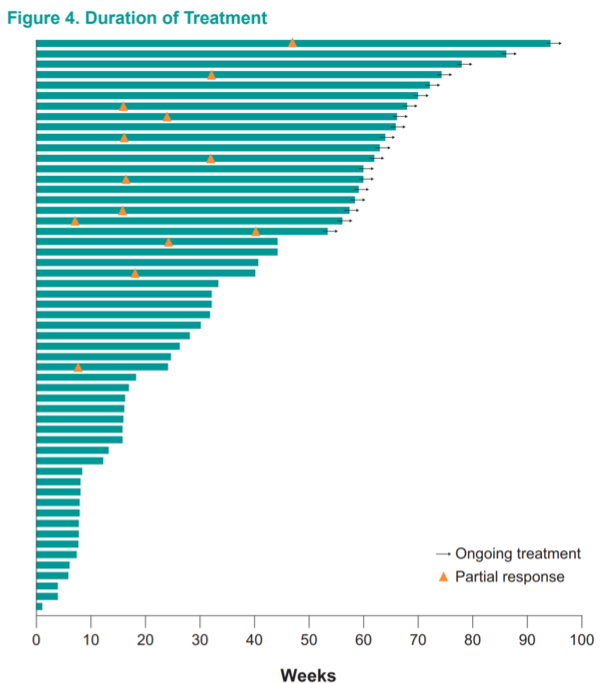
Remarkably, approximately half (49%) of these very heavily pretreated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma were alive and progression-free at 1 year.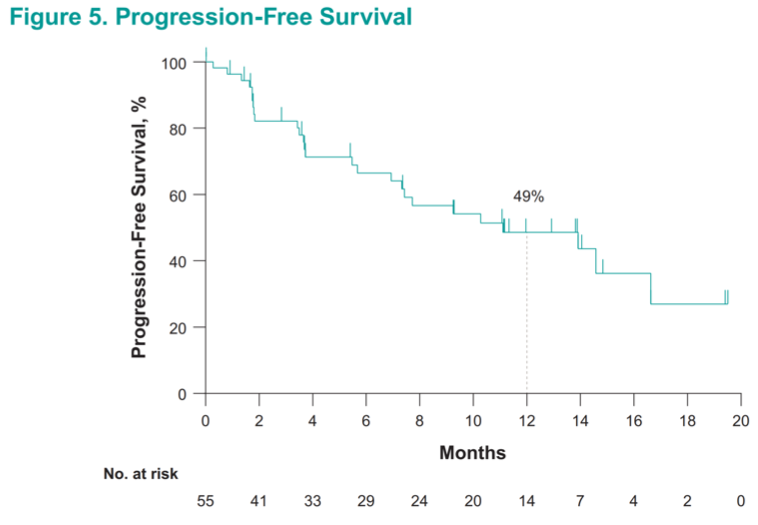
In summary, PT2977 was well-tolerated and lead to an encouraging response rate and progression-free survival in this phase II dose expansion cohort of heavily pretreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Follow-up data from this trial and additional studies with this agent in mRCC are eagerly anticipated.
Presented by: Eric Jonasch, MD, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, US
Written by: Michael Lattanzi, MD, Medical Oncology Fellow, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Twitter: @MikeLattanzi, at the 2019 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress (#ESMO19), September 27 – October 1, 2019, Barcelona, Spain
References:
- Sato Y, Yoshizato T, Shiraishi Y, Maekawa S, Okuno Y, Kamura T, Shimamura T, Sato-Otsubo A, Nagae G, Suzuki H, Nagata Y. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature genetics. 2013 Aug;45(8):860.
- Wallace EM, Rizzi JP, Han G, Wehn PM, Cao Z, Du X, Cheng T, Czerwinski RM, Dixon DD, Goggin BS, Grina JA. A small-molecule antagonist of HIF2α is efficacious in preclinical models of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer research. 2016 Sep 15;76(18):5491-500.


