(UroToday.com) Dr. Rusty Johnson, MD, PhD is a Medical Oncology Fellow at the Johns Hopkins Greenberg Bladder Cancer Institute in Baltimore, MD. He is the recipient of the 2020 BCAN Young Investigator Award for his research focused on the role of intratumoral B cell signatures on response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI).
B cells are a type of antigen-presenting cell (APC) heavily involved in immunogenicity. B cell subsets elicit a spectrum of immune responses from stimulation to inhibition. In a number of advanced solid malignancies, including melanoma and renal cell carcinoma, high concentrations of intratumoral B cells are associated with a favorable response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI).
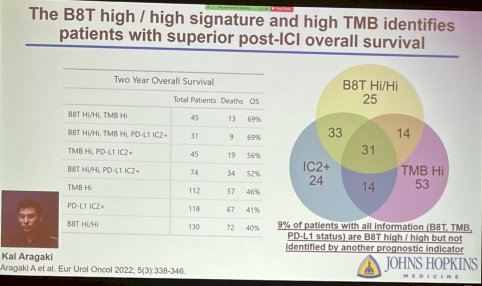
Dr. Johnson hypothesized that the intratumoral B cell/CD8+ T cell (B8T) signature is associated with response to ICI in patients with advanced bladder cancer. Using a cohort from the Phase II IMvigor2010 study of atezolizumab in locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer, patients were able to be subdivided into 4 groups based on B8T signature. These subgroups were closely associated with survival, with B8T Hi/Hi patients exhibiting the most favorable prognosis and Hi/Lo subgroup associated with poor survival.
The investigators then evaluated these phenotypes in subsets of patients. The favorable prognosis in B8T Hi/Hi patients was most prominent among patients with high tumor mutational burden (TMB) and PL-L1 positive tumors.
However, there was little prognostic utility in female patients compared to male patients treated with atezolizumab.
These findings were recently published in European Urology Oncology (2022) and have the possibility of identifying responders to systemic ICI therapy, and potentially inform the need for treatment alternatives and/or therapeutic intensification in inherent non-responders. Further investigation in this realm will use immunohistochemical markers (CD19 as a B cell marker and CD8 as a CD8+ T cell marker) to identify B8T signatures as a more economical and applicable alternative.
Presented by: Burles A. (Rusty) Johnson, III, MD, PhD, is a Medical Oncology Fellow at the Johns Hopkins Greenberg Bladder Cancer Institute in Baltimore, MD
Written by: Patrick Hensley, MD, Urologic Oncologist at the University of Kentucky (@pjhensley11) with Ashish Kamat, MD, Urologic Oncologist at MD Anderson Cancer Center (@UroDocAsh) during the 2022 Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network Think Tank (#BCANTT22) Wednesday, Aug 3 – Friday, Aug 5, 2022
References:
- Helmink BA, Reddy SM, Gao J, Zhang S, et al. B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response. Nature. 2020 Jan;577(7791):549-555. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1922-8. Epub 2020 Jan 15. PMID: 31942075; PMCID: PMC8762581.
- Aragaki AK, Jing Y, Hoffman-Censits J, et al. Gender-specific Stratification of Survival Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Based on Intratumoral Expression of a B cell Gene Signature. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022 Jun;5(3):338-346. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2021.07.003. Epub 2021 Aug 21. PMID: 34426176.


